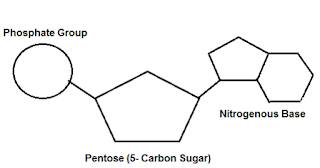
DNA polymerase:
-DNA polymerase is the enzyme that synthesizes new DNA molecules from the DNA nucleotides.
-DNA polymerase is the enzyme used in the DNA replication. Replication is process in which DNA is synthesized.
-DNA polymerase requires a primer for the initiation of polymerization
-DNA polymerase produces a double-stranded DNA molecule during polymerization.
-DNA polymerase synthesizes the entire chromosome.
RNA polymerase:
-RNA polymerase is the enzyme used in transcription. Transcription is process of synthesis of RNA molecules from.
-Both enzymes are capable of forming phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides
While RNA polymerases do not require primer.
-Whereas RNA polymerase produces single-stranded RNA molecule during transcription.
-RNA polymerase stops the synthesis at the transcription termination site